Mastering IP Address Management with Azure Virtual Network Manager IPAM
 Stephen Tulp
Stephen Tulp
January 21, 2026
5 minutes to read
Introduction
Managing IP address space across a growing Azure environment can quickly become a complex challenge. As organisations scale their cloud infrastructure, the need for a centralised, automated approach to IP Address Management (IPAM) becomes critical. Azure Virtual Network Manager (AVNM) now includes native IPAM capabilities that solve this challenge elegantly.
In this two-part series, we’ll dive deep into AVNM’s IPAM functionality, exploring its architecture, benefits, and how to implement it using Infrastructure as Code with Bicep and then update Azure Landing Zones to leverage AVNM IPAM for automated IP address allocation.
- Part 1: Overview of AVNM IPAM and Bicep implementation.
- Part 2: Integrating AVNM IPAM with Subscription Vending and Application Landing Zones for automated IP allocation.
What is Azure Virtual Network Manager?
Azure Virtual Network Manager (AVNM) is a centralised network management service that enables organisations to group, configure, deploy, and manage virtual networks at scale across subscriptions, regions, and tenants. It provides a unified control plane for defining network topologies, such as hub-and-spoke or mesh configurations, while enforcing consistent security policies through Security Admin Rules that take precedence over traditional Network Security Groups.
AVNM’s dynamic network group membership leverages Azure Policy conditions to automatically include virtual networks based on tags, subscriptions, or regions, eliminating manual network management overhead. With built-in support for User Defined Routing configurations and seamless integration with Azure Landing Zones, AVNM delivers network governance, enabling platform teams to maintain centralised control while empowering application teams with self-service networking within defined guardrails.
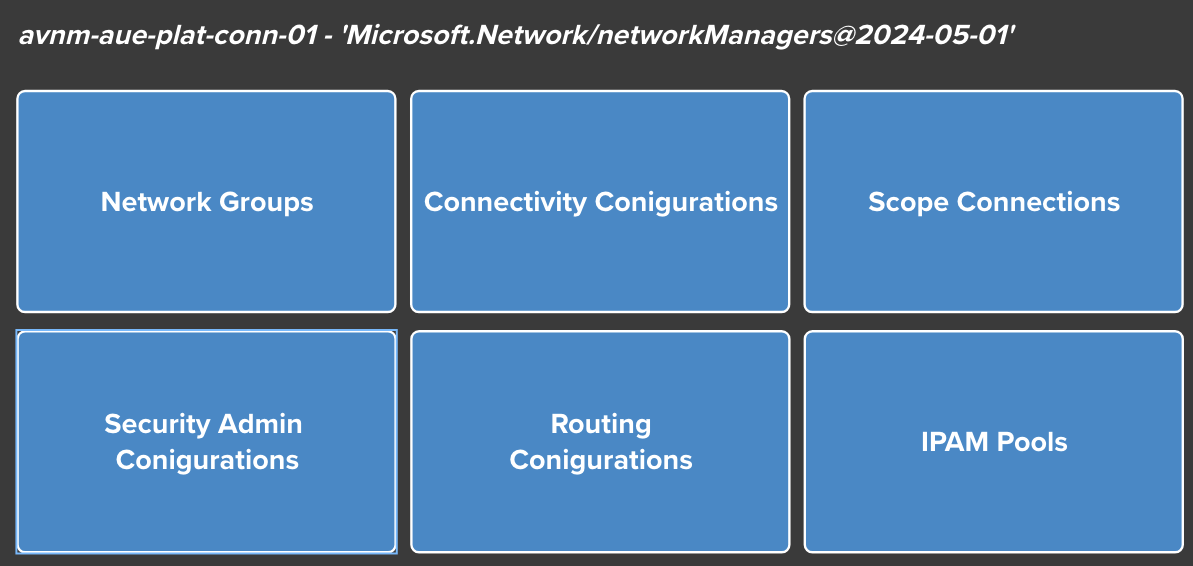
AVNM Architecture Overview
| AVNM Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Network Manager | The parent resource that defines the management scope (management group or subscription) |
| Network Groups | Collections of virtual networks for applying configurations (static or dynamic membership) |
| Connectivity Configurations | Define network topology (Hub-Spoke or Mesh) for network groups |
| Security Admin Configurations | Centralised security rules that are evaluated before NSGs |
| Deployments | Commits configurations to specific Azure regions |
| IPAM Pools | Hierarchical IP address pools for centralised address management |
| Routing Configurations | User-defined routes managed centrally across network groups |
The IPAM component of Azure Virtual Network Manager provides a centralised service for managing IP address allocation across your Azure environment. It allows you to:
- Define hierarchical IP address pools
- Allocate address spaces to virtual networks automatically
- Track IP address usage across subscriptions and regions
- Prevent overlapping address spaces
- Integrate with Azure landing zone architectures
Proposed AVNM IPAM Architecture
Inspiration and a starting point for this architecture comes from some great work by Pieterbas Nagengast Azure Virtual Network Manager IPAM documentation. Since the official Azure Network Manager module doesn’t yet support IPAM, I wanted to create something that uses Pieterbas’s work as a foundation but simplifies and focuses on a single region.
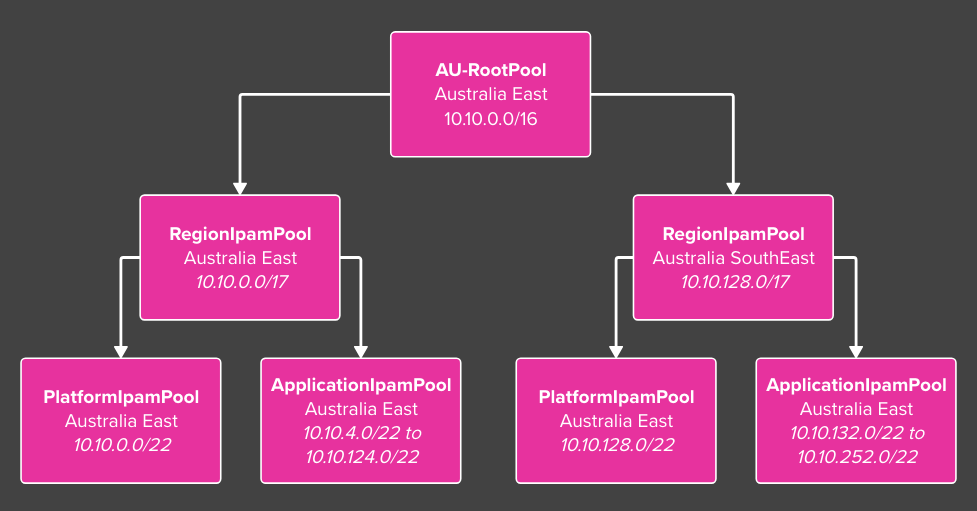
The diagram below illustrates the proposed AVNM IPAM architecture aligned with an Azure landing zone architecture, this differentiates between platform and application landing zones to allocate IP address space accordingly.
- A root IPAM pool representing the entire Australia (AU) Azure address space.
- Regional-specific IPAM pools for Australia East and Australia Southeast, carved out from the AU root pool.
- Each region pool is further divided into platform and application landing zone pools based on a configurable split.
- Platform landing zones receive
5%of the address space, while application landing zones receive the remaining95%. - This equates to a single
/22for Platform Landing Zones (Management, Connectivity, Identity). - This equates to 31 x
/22for Application Landing Zones.
- Platform landing zones receive
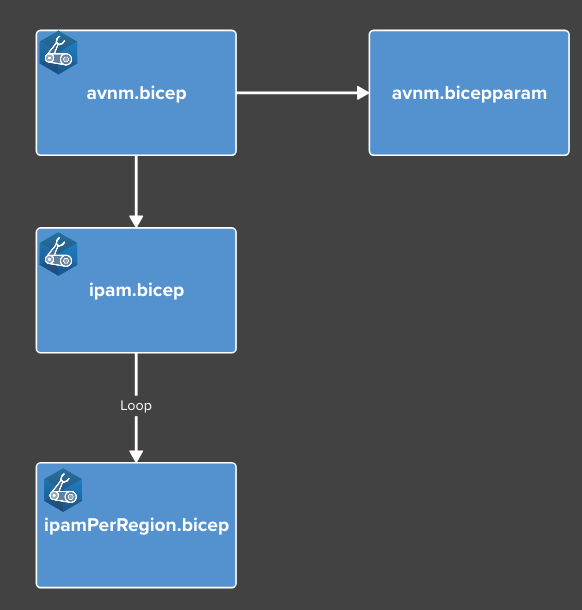
The Bicep templates are structured as follows:
avnm.bicep- The main Bicep file to deploy AVNM with IPAM pools and configurations.avnm.bicepparam- Parameter file for the deployment.ipam.bicep- Module to create the root IPAM pools.ipamPerRegion.bicep- Module to create regional IPAM pools that is looped for each Azure region defined in the parameter file.
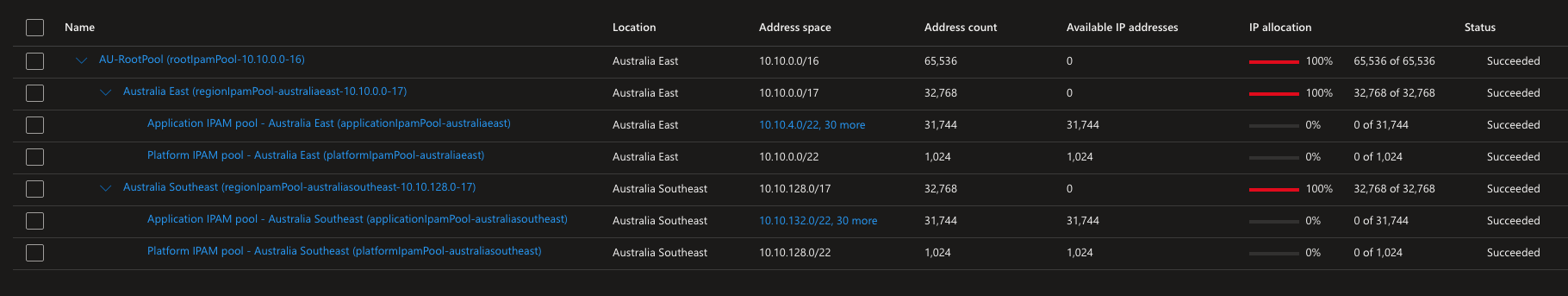
We can deploy the template directly in VS Code using the Bicep deployment pane feature, once complete we should have the full deployment and IPAM hierarchy created in AVNM and should look similar to below in the Azure Portal.
Conclusion
The Bicep templates and code can be found in my Repo. In the next post, we will integrate AVNM IPAM with Subscription Vending and Application Landing Zones for automated IP allocation of spoke virtual networks.